control.tf¶
- control.tf(*args)¶
Create a transfer function system. Can create MIMO systems.
The function accepts either 1 or 2 parameters:
- tf(sys)
- Convert a linear system into transfer function form. Always creates a new system, even if sys is already a TransferFunction object.
- tf(num, den)
Create a transfer function system from its numerator and denominator polynomial coefficients.
If num and den are 1D array_like objects, the function creates a SISO system.
To create a MIMO system, num and den need to be 2D nested lists of array_like objects. (A 3 dimensional data structure in total.) (For details see note below.)
- tf(num, den, dt)
- Create a discrete time transfer function system; dt can either be a positive number indicating the sampling time or ‘True’ if no specific timebase is given.
Parameters: sys: LTI (StateSpace or TransferFunction)
A linear system
num: array_like, or list of list of array_like
Polynomial coefficients of the numerator
den: array_like, or list of list of array_like
Polynomial coefficients of the denominator
Returns: out: TransferFunction
The new linear system
Raises: ValueError
if num and den have invalid or unequal dimensions
TypeError
if num or den are of incorrect type
Notes
num[i][j] contains the polynomial coefficients of the numerator for the transfer function from the (j+1)st input to the (i+1)st output. den[i][j] works the same way.
The list [2, 3, 4] denotes the polynomial
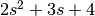 .
.Examples
>>> # Create a MIMO transfer function object >>> # The transfer function from the 2nd input to the 1st output is >>> # (3s + 4) / (6s^2 + 5s + 4). >>> num = [[[1., 2.], [3., 4.]], [[5., 6.], [7., 8.]]] >>> den = [[[9., 8., 7.], [6., 5., 4.]], [[3., 2., 1.], [-1., -2., -3.]]] >>> sys1 = tf(num, den)
>>> # Convert a StateSpace to a TransferFunction object. >>> sys_ss = ss("1. -2; 3. -4", "5.; 7", "6. 8", "9.") >>> sys2 = tf(sys1)